Heatmap#
For getting an idea of the distribution of values, heatmaps can be used.
Let us visualize some test data:
[1]:
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(1234)
F = np.random.random((4, 6))
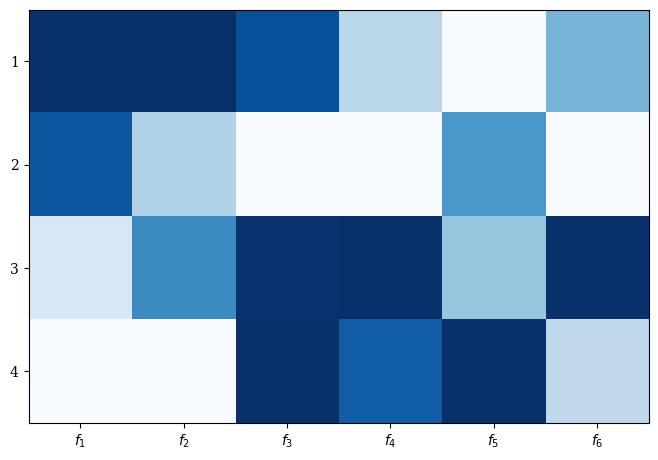
A simple heatmap can be created by:
[2]:
from pymoo.visualization.heatmap import Heatmap
Heatmap().add(F).show()
[2]:
<pymoo.visualization.heatmap.Heatmap at 0x1131e2660>
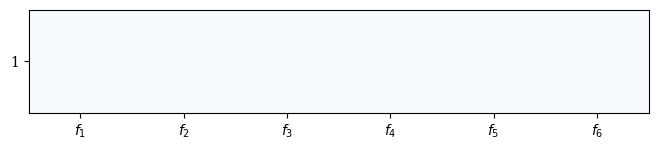
[3]:
Heatmap(bounds=[0,1]).add(np.ones((1, 6))).show()
[3]:
<pymoo.visualization.heatmap.Heatmap at 0x11106ae40>
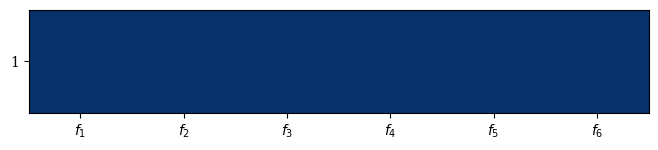
This behavior can be changed by setting reverse to False.
[4]:
Heatmap(bounds=[0,1],reverse=False).add(np.ones((1, 6))).show()
[4]:
<pymoo.visualization.heatmap.Heatmap at 0x11356ddc0>
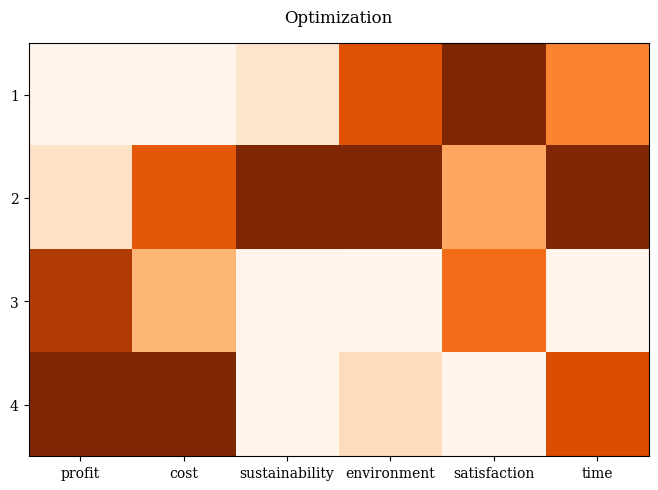
The plot can be further customized by supplying a title, labels, and by using the plotting directives from matplotlib. Also, colors can be changed:
[5]:
plot = Heatmap(title=("Optimization", {'pad': 15}),
cmap="Oranges_r",
solution_labels=["Solution A", "Solution B", "Solution C", "Solution D"],
labels=["profit", "cost", "sustainability", "environment", "satisfaction", "time"])
plot.add(F)
plot.show()
[5]:
<pymoo.visualization.heatmap.Heatmap at 0x113594380>
Moreover, the values can be sorted lexicographically by objective(s) - and by default, the selected objective is inserted in position 0 of the range of objectives. Also, boundaries can be changed. Otherwise, it is scaled according to the smallest and largest values supplied.
[6]:
F = np.random.random((30, 6))
plot = Heatmap(figsize=(10,30),
bounds=[0,1],
order_by_objectives=0,
solution_labels=None,
labels=["profit", "cost", "sustainability", "environment", "satisfaction", "time"],
cmap="Greens_r")
plot.add(F, aspect=0.2)
plot.show()
[6]:
<pymoo.visualization.heatmap.Heatmap at 0x1136eeea0>
API#
- class pymoo.visualization.heatmap.Heatmap(self, cmap='Blues', order_by_objectives=False, reverse=True, solution_labels=True, **kwargs)[source]
Heatmap
- Parameters:
- cmapstr
The color map to be used.
- order_by_objectivesint or list
Whether the result should be ordered by an objective. If false no order. Otherwise, either supply just the objective or a list. (it is lexicographically sorted).
- reversebool
If true large values are white and small values the corresponding color. Otherwise, the other way around.
- solution_labelsbool or list
If False no labels are plotted in the y axis. If true just the corresponding index. Otherwise, the label provided.
- boundstuple
If plot requires normalization, it might be necessary to supply the boundaries. (Otherwise they might be approximate by the minimum and maximum of the provided data). The boundaries should be provided as a list/tuple or 2D numpy array, where the first element represents the minimum, second the second the maximum values. If only an integer or float is supplied, the boundaries apply for each variable.
- labelsstr or list
The labels to be used for each variable provided in the plot. If a string is used, then they will be enumerated. Otherwise, a list equal to the number of variables can be provided directly.
- Other Parameters:
- figsizetuple
The figure size. Default (figsize=(8, 6)). For some plots changing the size might have side effects for position.
- titlestr or tuple
The title of the figure. If some additional kwargs should be provided this can be achieved by providing a tuple (“name”, {“key” : val}).
- legendstr
Whether a legend should be shown or not.
- tight_layoutbool
Whether tight layout should be used.
- cmapcolormap
For some plots different kind of colors are used. The colormap can be changed to modify the color sequence for the plots.