NRBO: Newton-Raphson-based Optimizer#
The Newton-Raphson-based Optimizer (NRBO) is a population-based metaheuristic algorithm for continuous optimization problems. It is inspired by the Newton-Raphson method used in numerical analysis for finding roots of real-valued functions. The algorithm combines the exploration capabilities of population-based methods with the exploitation power of gradient-based approaches.
Key Features#
Population-based approach: Maintains a population of solutions to explore the search space
Newton-Raphson Search Rule (NRSR): Utilizes a modified Newton-Raphson update rule for generating new solutions
Trap Avoidance Operator (TAO): Includes a mechanism to escape local optima
Dynamic adaptation: The algorithm adapts its search behavior based on the current iteration
Algorithm Parameters#
pop_size: Population size (number of individuals)deciding_factor: Control parameter for the Trap Avoidance Operator (default: 0.6)max_iteration: Maximum number of iterations (default: 100)sampling: Initial population sampling method (default: Latin Hypercube Sampling)
Example#
[1]:
from pymoo.algorithms.soo.nonconvex.nrbo import NRBO
from pymoo.problems import get_problem
from pymoo.optimize import minimize
# Define the problem
problem = get_problem("ackley", n_var=10)
# Initialize the algorithm
algorithm = NRBO(
pop_size=50,
deciding_factor=0.6,
max_iteration=100
)
# Perform the optimization
res = minimize(problem,
algorithm,
seed=1,
verbose=False)
print("Best solution found: \nX = %s\nF = %s" % (res.X, res.F))
Best solution found:
X = [-2.52476988e-17 -7.98127053e-17 -6.27542596e-17 9.29501856e-17
5.83659862e-17 -6.40720275e-18 8.12597512e-17 1.04586871e-16
7.70446713e-18 4.10074262e-17]
F = [4.4408921e-16]
Constrained Optimization Example#
NRBO can also handle constrained optimization problems:
[2]:
from pymoo.algorithms.soo.nonconvex.nrbo import NRBO
from pymoo.problems import get_problem
from pymoo.optimize import minimize
# Define a constrained problem
problem = get_problem("g1")
# Initialize the algorithm
algorithm = NRBO(
pop_size=100,
deciding_factor=0.6,
max_iteration=200
)
# Perform the optimization
res = minimize(problem,
algorithm,
seed=1,
verbose=False)
print("Best solution found:")
print("X = %s" % res.X)
print("F = %s" % res.F)
print("Constraint violation: %s" % res.CV)
Best solution found:
X = [1. 0.9999999 0.99999992 1. 0.9999976 0.99999818
0.99999997 0.99999645 0.99999879 2.99999757 2.99999633 2.99942567
1. ]
F = [-14.99940958]
Constraint violation: [0.]
Performance Comparison#
Here’s an example comparing NRBO with other single-objective algorithms:
[3]:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pymoo.algorithms.soo.nonconvex.nrbo import NRBO
from pymoo.algorithms.soo.nonconvex.ga import GA
from pymoo.algorithms.soo.nonconvex.pso import PSO
from pymoo.problems import get_problem
from pymoo.optimize import minimize
# Define the problem
problem = get_problem("rastrigin", n_var=10)
# Define algorithms
algorithms = [
("NRBO", NRBO(pop_size=50)),
("GA", GA(pop_size=50)),
("PSO", PSO(pop_size=50))
]
# Run optimizations and collect results
results = {}
for name, algorithm in algorithms:
res = minimize(problem,
algorithm,
termination=('n_gen', 100),
seed=1,
save_history=True,
verbose=False)
results[name] = res
# Plot convergence
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
for name, res in results.items():
n_evals = [e.evaluator.n_eval for e in res.history]
opt = [e.opt[0].F for e in res.history]
plt.plot(n_evals, opt, label=name, linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel("Number of Evaluations")
plt.ylabel("Best Fitness Value")
plt.title("Convergence Comparison on Rastrigin Function (10D)")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.yscale('log')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Print final results
print("\nFinal Results:")
for name, res in results.items():
print(f"{name}: F = {res.F[0]:.6f}")
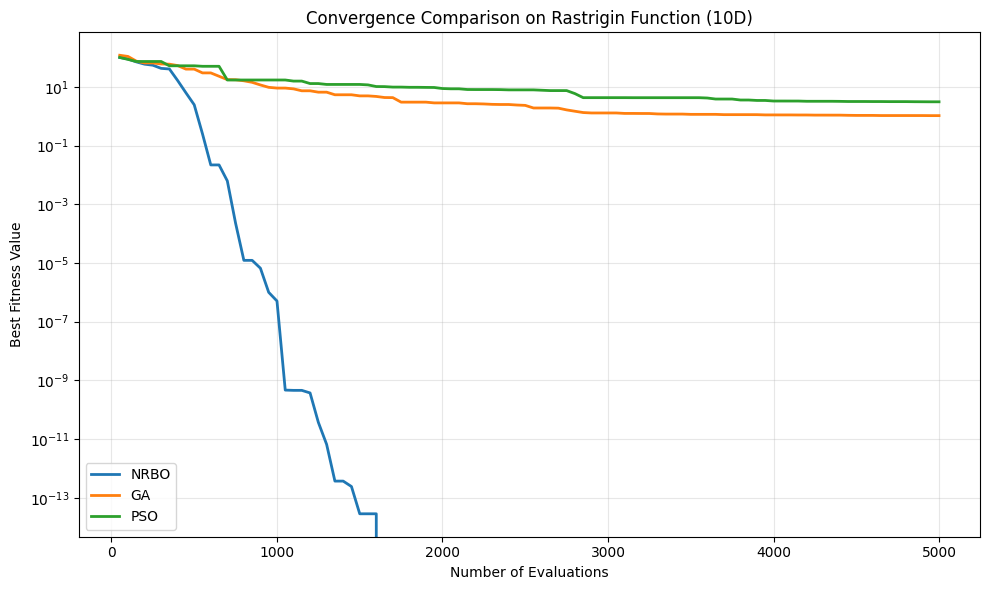
Final Results:
NRBO: F = 0.000000
GA: F = 1.045773
PSO: F = 3.092620
API#
- pymoo.algorithms.soo.nonconvex.nrbo.NRBO(pop_size=50, deciding_factor=0.6, sampling=<pymoo.operators.sampling.lhs.LHS object>, max_iteration=100, repair=<pymoo.core.repair.NoRepair object>, output=None, display=None, callback=None, archive=None, return_least_infeasible=False, save_history=False, verbose=False, seed=None, evaluator=None, **kwargs)[source]
References#
The Newton-Raphson-based Optimizer (NRBO) was proposed in [24].
Acknowledgments#
Note
We would like to thank @Zcaic for contributing the NRBO implementation to pymoo.